What is Grid trading system?
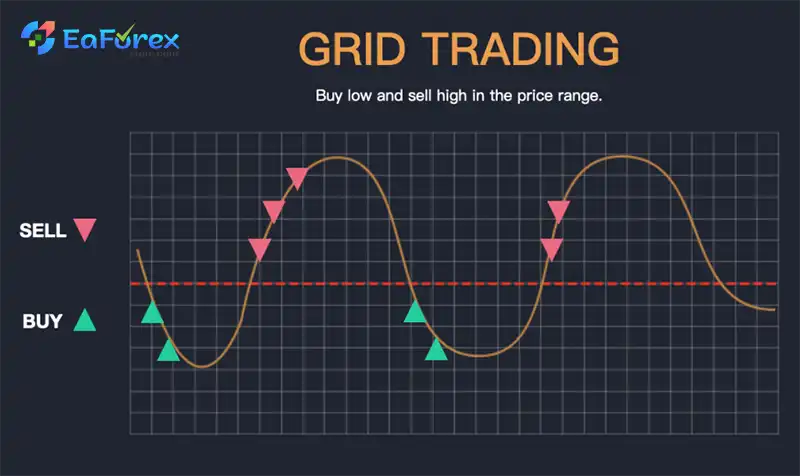
What is Grid trading?
Grid trading is a trading strategy that involves placing buy and sell orders at predetermined intervals above and below a specific price, creating a “grid” of orders. This strategy aims to profit from price fluctuations without requiring precise market direction predictions. Grid trading is commonly used in the foreign exchange market but can be applied to other financial instruments as well.
How Does Grid Trading Work?
- Setting the Grid: A trader establishes a base price and determines the interval between orders (e.g., 10 pips, 50 pips).
- Placing Orders: Buy and sell orders are placed at regular intervals above and below the base price, forming a grid.
- Profiting from Price Fluctuations: As the price fluctuates within the grid, the orders are triggered, leading to potential profits.
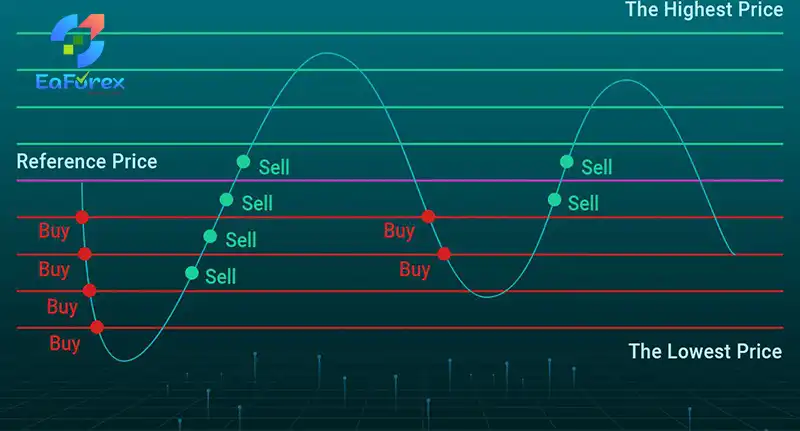
Types of Grid Trading
- With-the-Trend Grid: Buy orders are placed above the base price, and sell orders below. This strategy aims to profit from sustained price movements in a particular direction.
- Against-the-Trend Grid: Buy orders are placed below the base price, and sell orders above. This strategy seeks to profit from price reversals or sideways movements.
Key Considerations
- Risk Management: Setting appropriate stop-loss orders is crucial to limit potential losses.
- Market Conditions: Grid trading is most effective in markets with consistent price fluctuations.
- Automation: Grid trading can be automated using trading platforms, reducing manual intervention.
Conclusion
Grid trading offers a systematic approach to trading, aiming to capitalize on price fluctuations. While it can be a profitable strategy, it’s essential to understand its risks and limitations. By carefully setting up the grid, managing risk effectively, and monitoring market conditions, traders can potentially benefit from this strategy.